TARA in ISO 21434, the analysis of cyber risks and threats
The TARA (Threat Analyses and Risk Assessment) analysis is the method specified by ISO 21434 for analyzing the threats and risks present in automotive digital security components, with the aim of ensuring the cybersecurity of newly approved cars.
When to use automotive TARA analysis
From the initial concept phase of an electrical or electronic product aimed at the car market, it is necessary to determine what cybersecurity goals the element must ensure.
Based on the threat and risk assessment (TARA, given in clause 15 of ISO 21434), here are the cybersecurity goals which should be considered as the highest level requirements for each item, the component that performs safety functions inside the vehicle, as defined by ISO 21434.

The goals will then be detailed within the subsequent cybersecurity specification, following the process above.
The definition of the item
The definition of the Item goes through a few stages, the key ones of which are:
- Establishing the operating environment, including interfaces with other elements inside the vehicle and/or with the E/E system outside it
- Describing the expected behavior of the component during the different stages of the lifecycle such as product development, manufacturing, operation and maintenance
- Determining the preliminary architecture
- Identifying components and connections
Do you want to contribute to our page?
Follow us on LinkedinProcess for the TARA analysis in ISO 21434
After defining the item, the expected features and functionality of the system will have been made available; the TARA analysis is now required to analyze its cyber threats and risks; the result of the analysis lays the foundation for defining the cybersecurity goals and for the realization of the product that will follow.
These are examples of expected goals after the TARA analysis:
- Preventing insufficient lateral adjustment that results in drifting off the roadway when an automatic lane centering system is activated
- Preventing excessive lateral adjustment that results in leaving the roadway when an automatic lane centering system is activated
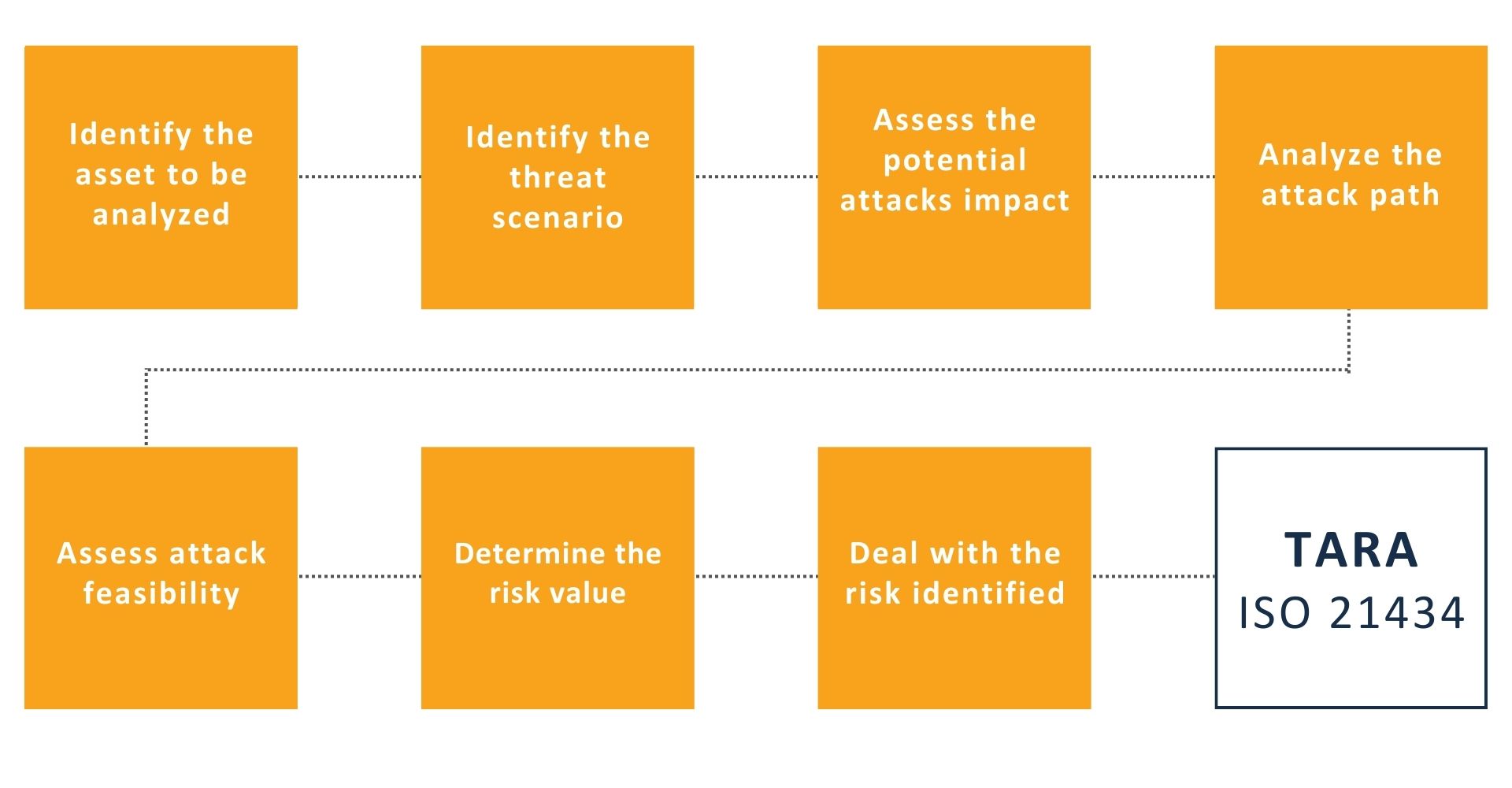
This is the TARA process, aimed at deriving risk treatment decisions and, consequently, security countermeasures to be implemented in product design.